The popularity of the flexible approach is growing — according to a Preferred Office Network study, flexible workspaces have emerged and the market continues to develop dynamically, expected to grow further in 2025. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of flexible office spaces, their advantages, and the potential challenges that may arise in the flexible workspace industry, highlighting how office design can influence overall productivity.
What Is Flexible Office Space?
Flexible office space is a contemporary commercial real estate model that offers adaptable and customizable work environments by transforming large vacant buildings, such as old office centers or factories, into smaller, leasable sections. Flex office space provides short-term leases and customizable layouts, making it suitable for dynamic work environments such as startups and freelancing. Companies can tailor their office solutions by selecting specific areas like meeting rooms and common spaces to meet their unique needs.

Key Benefits of Flexible Workspaces
Productivity
A flexible office layout boosts focus and fosters collaboration. Instead of fixed work areas, each space is tailored to specific tasks: a large conference room for development teams, an open creative zone for marketers, and quiet pods for concentrated work where employees need to concentrate without distractions.
Case Study — Seasonal Adjustments
Companies can use multi-purpose rooms and lightweight storage modules to expand workspace when needed and revert to a compact setup at no extra cost, keeping teams focused in the optimal environment.
Cost-Efficiency
Only pay for the space you need. If your team grows, add more desks; if it shrinks, free up unused areas. This agility benefits startups and small businesses, as well as projects with strong seasonal demands.
Case Study — Holiday Services Agency
During peak season (e.g., New Year holidays), they hire temporary staff and easily accommodate them without long-term rental agreements. Post-season, they release extra workstations to avoid paying for idle space.
Rapid Scaling
Flexible formats let companies respond swiftly to business changes, which makes flexible office spaces crucial for agile growth. Unlike traditional offices with a fixed location and designated cubicles, flexible workspaces offer greater adaptability and responsiveness to change. When a major client signs on, simply rent additional space in the same building or set up a few extra modern workstations — no lengthy searches or remodels required.
Case Study — Department Reorganization
If resources shift from one office to another, adaptable spaces mean renting only as many spots as needed in a nearby center, minimizing downtime and bureaucracy.
Employee Wellness
A variety of work and relaxation areas promotes well-being by balancing focus and leisure. Natural light, comfortable furniture, and flexible layouts reduce stress and keep employees happy and productive.
Case Study — Lounge & Work Areas
By creating zones with ample light, ergonomic desks, and comfortable seating, employees can move between open spaces for collaboration, quiet corners for deep focus, and cozy lounges for breaks—leading to lower stress, higher satisfaction, and improved overall output.
Types of Flexible Workspaces
Serviced Office
Ideal for: Businesses expanding into new markets and needing a ready-to-use workspace quickly.
A serviced office is fully furnished, with internet and cleaning on flexible lease terms. It allows immediate startup without extra infrastructure costs.
Coworking Spaces
Ideal for: Freelancers, remote workers, startups, and small teams seeking a collaborative environment.
These shared spaces offer open areas, communal resources, and networking opportunities, forming a flexible coworking setting. Memberships are flexible, and amenities like internet and meeting rooms are included.
Private/Managed Office
Ideal for: Medium and large companies that value confidentiality and quiet. Private office space within a larger workspace, providing stability through long-term lease agreements. The operator handles furnishing, internet, and cleaning.
Hot-Desking
Ideal for: Outsourced specialists requiring flexible infrastructure without extra costs.
Employees use any open spot in a shared area, whether you need a quick touchdown desk or a more permanent workstation, accessing the internet and common facilities like meeting rooms and kitchens.
Hybrid Workspaces
Ideal for: Teams balancing remote flexibility with on-site collaboration.
Employees split their time between working from home and using physical office setups, whether you need a quiet spot for focused tasks or a collaborative environment for brainstorming.
Event Spaces/Meeting Rooms
Ideal for: Organizers needing equipped halls for short-term events or training sessions.
Rooms rented by the hour or day, fully furnished, with technology and furniture that can be rearranged as needed.
Pop-up Spaces and Commercial Areas
Ideal for: Brands testing new products or running short-term promotions.
Short-term rentals in high-traffic locations, perfect for measuring demand without the need for long-term commitments.
Differences Between Flexible Workspaces and Traditional Offices
Rental System. In the classic model of traditional office space, companies sign a rent for a year (or longer) and pay for a fixed amount of space. If the team size changes, they either overpay for vacant space or urgently search for a new office. The flexible model is simpler:
- When downsizing, you can relinquish part of the space;
- When expanding, you can quickly rent a few more square meters or meeting rooms.
To optimize the rental process and manage space changes, companies can use workspace strategies with office work analytics. This tool provides detailed data on office space occupancy, allowing precise forecasting of space needs and informed leasing decisions.
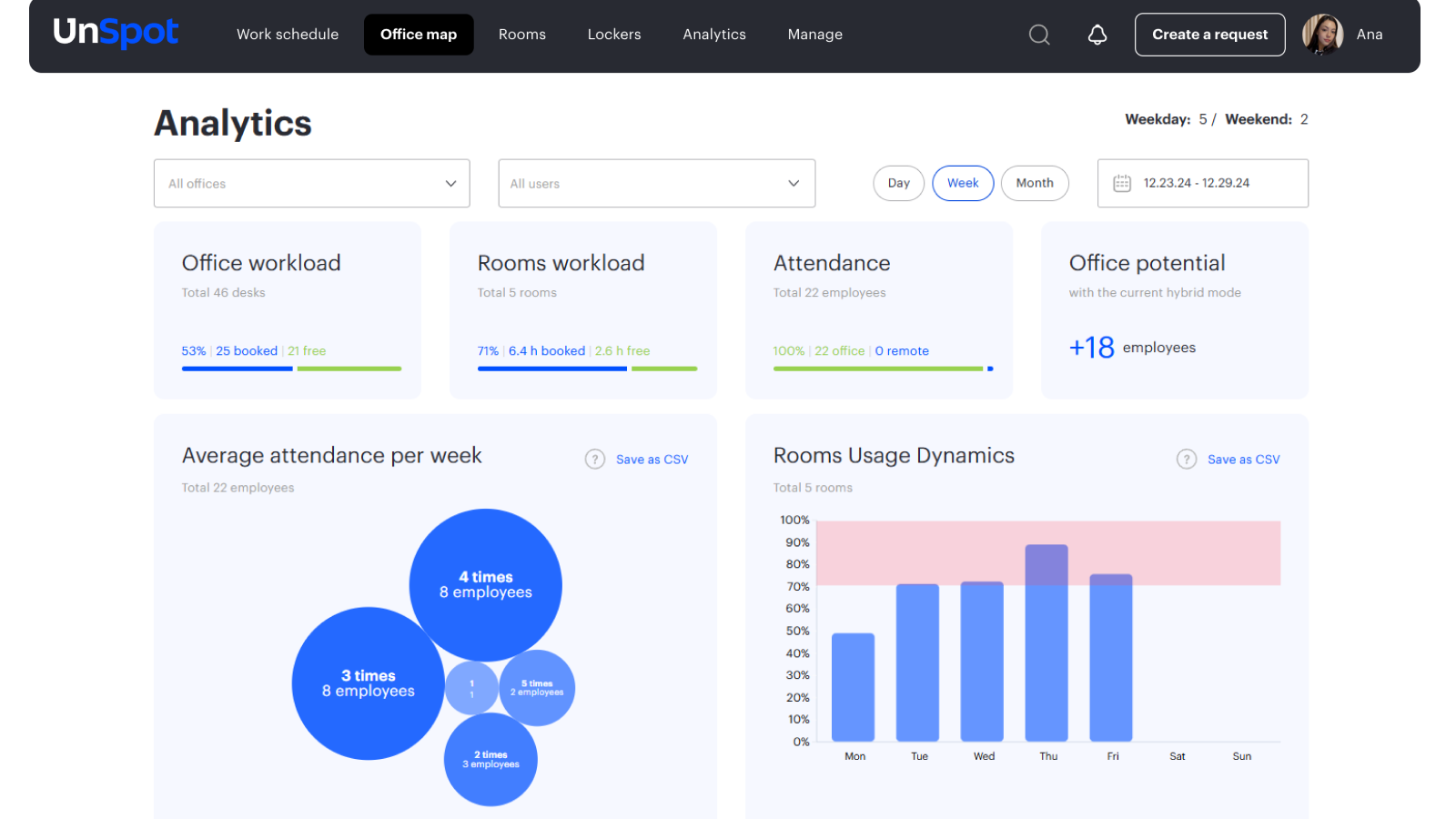
Building Formats. Traditional offices are typically located in standard business centers, where tenants take a "shell" and handle renovations and furnishing themselves. Flexible spaces are usually created in unused industrial buildings or old office buildings, which are renovated and equipped with everything needed.
Customization. Traditional office spaces often have pre-designed layouts that may not suit a specific team. In adaptable spaces, everything is different:
- The company determines how many conference rooms it needs;
- You can quickly add a lounge area or a few additional workstations;
- If the team shrinks, part of the space is freed up and removed from the lease.
Cost and Maintenance Terms. In a traditional office, expenses for internet, cleaning, and equipment maintenance are entirely the tenant's responsibility. Flexible spaces mean that most "housekeeping" issues are handled by the management company. Additionally, rent can be adjusted through flexible contracts according to current needs, allowing savings and avoiding overpayment for extra meters.
Gathered all the differences of work formats in one table, check it out ⬇️
| Criterion | Traditional Office | Flexible Office |
| Rental System | Long-term lease with fixed space. | Flexible contracts with the ability to adjust space as needed. |
| Building Formats | Located in standard business centers, requiring self-renovation and furnishing. | Utilizes renovated buildings with ready infrastructure (furniture, Wi-Fi, conference rooms). |
| Customization | Pre-designed layouts, limited adaptation to team needs. | High flexibility: adding or reducing workstations, conference rooms, and lounge areas on demand. |
| Cost and Maintenance | Full responsibility of the tenant for internet, cleaning, and technical maintenance. | Management company handles most maintenance tasks; rent adjusts according to current needs, allowing savings. |
| Space Management | Labor-intensive process when changing team size. | Use of analytics to optimize space usage and quickly respond to changes. |
Importance of Office Layout in Flexible Workspaces
The layout influences more than just seating — it affects employees’ mood, motivation, and productivity. Thoughtful desk, meeting room, and relaxation area arrangements support both quiet focus and easy collaboration.
For instance, having a nearby conference room with movable furniture lets a small team gather quickly without disturbing others. Conversely, relying on only one constantly occupied conference room can waste time and disrupt workflows.
With a flexible layout, you can create distinct zones for different work needs:
- Quiet Areas: For calls or tasks requiring deep concentration.
- Open Space: For teams that need quick communication.
- Common Areas: Where employees from different departments can exchange ideas.
The result is a convenient work environment where everyone knows where to find privacy or join colleagues, ultimately saving time and boosting team efficiency.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Flexible Workspaces
Lack of Available Space
Sometimes a company hires new employees but lacks sufficient space; the current office is too small, and there are no adjacent areas to expand.
How to Solve:
- Reserve Additional Space in Advance: When signing the lease, arrange to be on a waiting list for nearby areas.
- Choose a Backup Location: Consider multiple locations or flexible configurations to quickly relocate some employees if needed.
Lack of Privacy
Open, adaptable spaces can be crowded and noisy, making it difficult to maintain confidentiality and focus.
How to Solve:
- Rent Private Offices or Pods: Provide dedicated areas where conversations won’t be overheard.
- Use Noise-Canceling Technologies: Install partitions, sound-absorbing furniture, and provide headphones.
To enhance privacy management in the office, we recommend installing a display in front of conference rooms. This way, employees can see the availability of conference rooms in real-time and know exactly when they will be free.
Rising Rental Costs
Rental rates may rise if the building becomes popular or if demand for flexible workspaces increases.
How to Solve:
- Lock in Details in the Contract: Specify permissible price increases or early notice requirements.
- Allocate a Budget for Unexpected Costs: Keep a reserve in case rent goes up suddenly.
Limitations of Old Buildings
Older buildings often have outdated infrastructure and aren’t designed for modern office requirements (e.g., weak ventilation, old wiring).
How to Solve:
- Inspect Buildings Before Leasing: Request technical documentation and confirm fire safety and ventilation standards.
- Create a Backup Communication Plan: Prepare extra heating or ventilation equipment for extreme weather conditions.
Real-Life Examples of Flexible Offices in Action
Flexible spaces in the USA are often created in former industrial or administrative buildings that are no longer in use. Major networks do this, for example:
Industrious
Specializes in redevelopment: takes old factories and warehouses in Detroit, Chicago, Seattle, and other cities, transforming them into cozy workspaces with interior design finishes and ready infrastructure. If a tenant's team size decreases, they can easily reduce the leased block and pay less.
Spaces (IWG)
Invests in properties that have lost market appeal (like old business centers), updates the facades and interiors, and maintains the ability to "mix" zones: you can rent one conference room and add a hundred square meters of open space.
Galvanize
Focused on tech companies and educational initiatives, they renovate former warehouses and industrial sites into trendy campuses with common areas, classrooms, and office segments. Startups that don't need the entire space can rent just one floor or even half a floor and quickly add more rooms as they grow.
📝 Core Concept
Owners purchase and renovate unused buildings, dividing them into various functional zones. Tenants can rent exactly the space they need without long-term commitments, flexible workspaces allow them to easily adjust their space as their company grows or downsizes. This flexibility offers greater freedom and cost savings compared to traditional offices.
The Future of Flexible Office Spaces
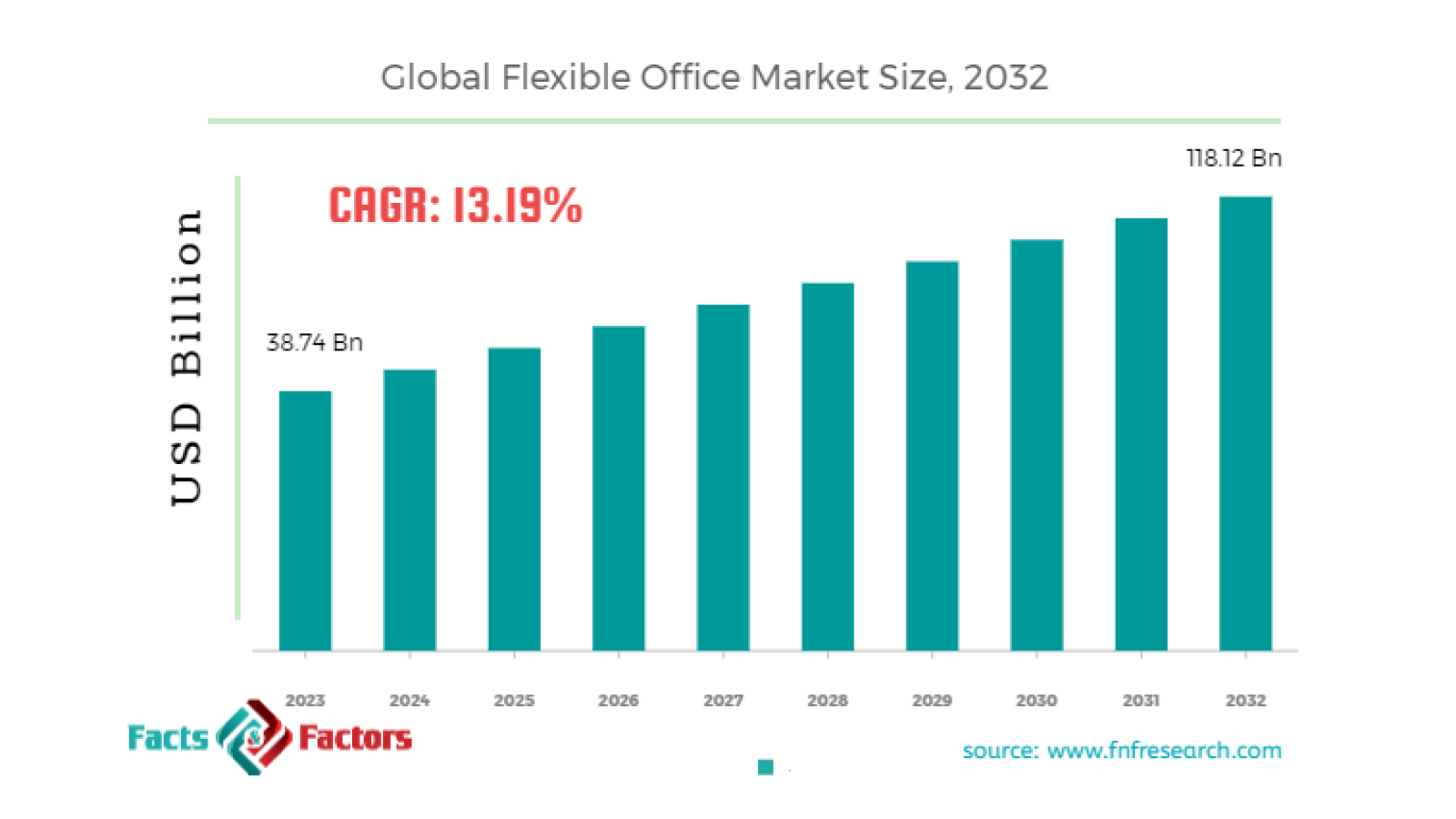
According to a study by FNF Research, an expert in real estate market analysis, flexible workspaces are becoming a key factor in transforming the office ecosystem. The report emphasizes that the flexible office market is rapidly growing: its volume, which was USD 38.74 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 118.12 billion by 2032, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.19%.
Key Findings of the Study
- Rising Demand for Hybrid Work Models. By 2025, it is expected that 45% of companies will implement hybrid work models, significantly increasing the need for flexible office spaces.
- Integration of Technologies. More than 70% of flexible offices already use analytical tools and IoT devices to monitor space utilization, allowing for a reduction in operational costs by 15-20%.
- Increased Focus on ESG Practices. Approximately 55% of flexible office spaces have implemented energy-efficient solutions and participate in ESG initiatives, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint and enhancing attractiveness for environmentally conscious companies.
Main Thing About Flexible Workspaces
- Flexible office spaces allow businesses to quickly adapt to changes, scale up, and reduce costs through flexible leasing.
- The main advantages of flexible offices include cost reduction, rapid expansion, and open layout, making them essential for the future of work.
- There are six flexible office types: serviced offices, coworkings, private/managed offices, hot desks, event spaces, and pop-up areas, catering to different business needs.
- Unlike traditional offices, adaptable spaces offer ready infrastructure, the ability to quickly adjust leased areas, and better savings on maintenance.